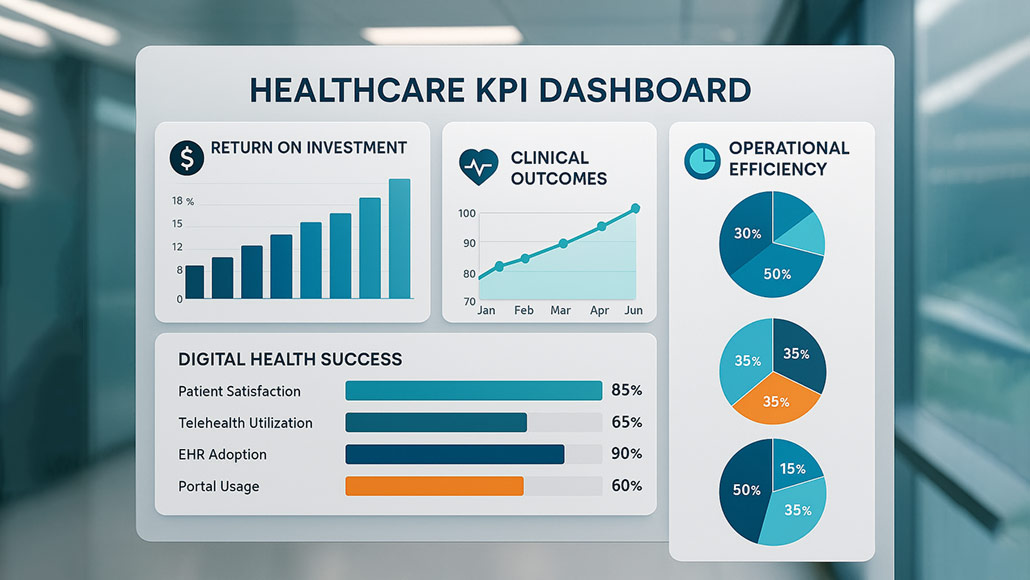
Measuring Success: KPIs and Metrics for Digital Health Initiatives
The measurement and evaluation of digital health initiatives has evolved into a sophisticated discipline that requires comprehensive understanding of performance indicators, analytical methodologies, and measurement frameworks that capture the multifaceted impact of technology investments on clinical outcomes, operational efficiency, and strategic objectives. Digital health KPIs metrics measurement encompasses far more than traditional technology performance indicators to include clinical effectiveness measures, patient experience assessments, financial impact analysis, and organizational transformation indicators that collectively demonstrate the value and success of healthcare technology initiatives.
Modern healthcare organizations invest billions of dollars annually in digital health technologies including Electronic Health Records, telemedicine platforms, artificial intelligence applications, remote monitoring systems, and patient engagement tools while facing increasing pressure to demonstrate measurable returns on these investments. The complexity of healthcare environments means that digital health success cannot be measured through simple metrics alone but requires sophisticated measurement frameworks that address clinical quality, patient outcomes, operational performance, and strategic alignment simultaneously.
Hospital executives and healthcare administrators increasingly recognize that effective measurement of digital health initiatives requires comprehensive approaches that balance quantitative analytics with qualitative assessments while addressing both immediate operational impacts and long-term strategic benefits. The challenge lies in developing measurement strategies that capture the true value of digital health investments while providing actionable insights that guide continued investment decisions and optimization efforts in an increasingly competitive and resource-constrained healthcare environment.
Establishing Digital Health Measurement Frameworks
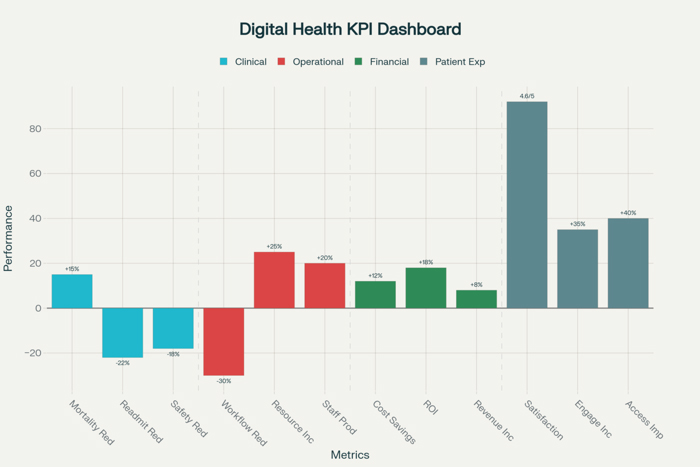
Successful measurement of digital health initiatives begins with comprehensive frameworks that define success criteria, establish measurement methodologies, and create systematic approaches for collecting, analyzing, and reporting performance data across multiple dimensions of healthcare delivery and organizational performance. These frameworks must address the unique characteristics of healthcare environments while providing practical guidance for measuring complex, interconnected technology initiatives that impact clinical care, operational efficiency, and strategic objectives simultaneously.
Strategic alignment assessment ensures that digital health measurement frameworks address organizational priorities, strategic objectives, and stakeholder expectations while providing evidence that technology investments support broader healthcare goals including quality improvement, cost management, patient satisfaction, and competitive positioning. This alignment should connect digital health metrics to organizational mission, vision, and strategic plans while demonstrating how technology initiatives contribute to overall organizational success.
Measurement hierarchy development establishes relationships between different levels of performance indicators including strategic metrics that address organizational objectives, operational metrics that track process efficiency and effectiveness, and tactical metrics that monitor specific technology performance and user adoption. This hierarchy should provide clear connections between high-level strategic goals and detailed operational measurements while enabling both executive oversight and operational management.
Stakeholder perspective integration ensures that digital health measurement frameworks address the diverse needs and interests of different stakeholder groups including patients, clinicians, administrators, and technology teams who may have different priorities and success criteria for digital health initiatives. These frameworks should provide relevant metrics for each stakeholder group while maintaining comprehensive assessment of overall program performance and value.
Baseline establishment and benchmarking create reference points for measuring improvement and comparing performance against industry standards, best practices, and peer organizations while providing context for interpreting measurement results. These baselines should capture pre-implementation performance levels while identifying appropriate comparison groups and benchmark data sources that support meaningful performance assessment.
Clinical Outcome and Quality Metrics
The measurement of clinical outcomes and quality improvements represents the most critical dimension of digital health KPIs metrics measurement because the ultimate value of healthcare technology must be demonstrated through improved patient health, enhanced care quality, and better clinical outcomes. These clinical metrics must address both process improvements and outcome enhancements while providing evidence that digital health investments translate into tangible benefits for patient care and health outcomes.
Patient outcome indicators measure the direct impact of digital health initiatives on health results including mortality rates, morbidity indicators, functional status improvements, quality of life measures, and disease-specific outcomes that reflect the effectiveness of technology-enhanced care delivery. These outcome metrics should address both short-term clinical improvements and long-term health benefits while controlling for confounding factors that might influence patient outcomes independent of digital health interventions.
Care quality metrics assess how digital health initiatives impact adherence to evidence-based care protocols, clinical guidelines, and quality standards while measuring improvements in care consistency, accuracy, and comprehensiveness. These quality indicators should address process measures such as medication administration accuracy, diagnostic test ordering appropriateness, and care coordination effectiveness that influence the likelihood of achieving desired patient outcomes.
Patient safety indicators specifically measure how digital health initiatives impact adverse events, medical errors, and safety-related incidents while assessing improvements in safety processes and risk mitigation strategies. These safety metrics should include medication error rates, hospital-acquired infection rates, patient fall incidents, and other safety events that digital health technologies are designed to prevent or reduce.
Clinical efficiency measures assess how digital health initiatives improve clinical workflow efficiency, reduce unnecessary procedures, and optimize resource utilization while maintaining or enhancing care quality. These efficiency indicators should address factors such as diagnostic turnaround times, treatment delay reductions, and care coordination improvements that demonstrate operational benefits of digital health investments.
Operational Performance and Efficiency Indicators
Digital health initiatives often generate significant operational improvements that must be measured and documented to demonstrate comprehensive value beyond clinical outcomes alone. Operational performance metrics address how technology investments impact healthcare delivery processes, resource utilization, staff productivity, and organizational efficiency while providing evidence of systematic improvements that support better patient care and cost management.
Workflow efficiency metrics measure improvements in care delivery processes including reduced documentation time, streamlined communication, automated routine tasks, and eliminated redundant activities that enable healthcare providers to focus more time and attention on direct patient care. These efficiency measures should quantify time savings, process improvements, and workflow optimization that result from digital health implementations.
Resource utilization indicators assess how digital health initiatives impact the use of hospital resources including staff time, equipment utilization, facility capacity, and supply consumption while identifying opportunities for optimization and cost reduction. These utilization metrics should address both direct resource impacts and indirect effects that result from improved efficiency and care coordination.
Staff productivity measurements evaluate how digital health technologies impact healthcare provider productivity including patient volume capacity, care delivery efficiency, and administrative task completion while assessing whether technology investments enable providers to deliver more effective care with available resources. These productivity indicators should address both quantitative output measures and qualitative assessments of work satisfaction and effectiveness.
Operational cost analysis examines how digital health initiatives impact direct operational expenses including labor costs, supply expenses, equipment utilization costs, and overhead allocations while identifying cost savings opportunities and efficiency gains. These cost measures should provide comprehensive assessment of financial impact while addressing both immediate cost effects and long-term operational benefits.
Patient Experience and Engagement Measurements
Patient experience and engagement metrics provide essential perspectives on digital health success because technology initiatives must ultimately serve patient needs and preferences while enhancing rather than complicating patient interactions with healthcare services. These patient-centered measurements address satisfaction levels, engagement patterns, and experience quality that reflect the patient perspective on digital health value and effectiveness.
Patient satisfaction indicators measure patient perceptions of digital health services including usability assessments, convenience ratings, communication quality evaluations, and overall satisfaction with technology-enhanced care delivery. These satisfaction measures should capture patient feedback on specific digital health tools while assessing overall impact on care experience quality and patient-provider relationships.
Digital engagement metrics track patient utilization of digital health services including portal usage rates, mobile application adoption, telemedicine participation, and self-service feature utilization while measuring engagement depth and frequency that indicate patient value perception and technology acceptance. These engagement indicators should provide insights into patient preferences and behavior patterns while identifying opportunities for enhancement and optimization.
Access and convenience measures assess how digital health initiatives improve patient access to healthcare services including reduced travel requirements, expanded service hours, shortened wait times, and enhanced appointment availability while measuring improvements in care accessibility for diverse patient populations. These access metrics should address both quantitative improvements and qualitative patient feedback on convenience and accessibility enhancements.
Patient empowerment and activation indicators evaluate how digital health tools enable patients to take more active roles in their care management including self-monitoring capabilities, educational resource utilization, care plan participation, and shared decision-making involvement. These empowerment measures should assess both patient capability development and actual engagement in self-care activities that support better health outcomes.
Financial Performance and Return on Investment
Comprehensive financial measurement of digital health initiatives requires sophisticated approaches that capture both direct cost impacts and indirect financial benefits while providing clear evidence of return on investment that justifies technology expenditures and supports continued investment in digital health capabilities. These financial metrics must address implementation costs, operational savings, revenue enhancements, and long-term financial benefits that result from digital health investments.
Implementation cost tracking provides detailed accounting of all expenses associated with digital health initiatives including technology acquisition, implementation services, training costs, infrastructure upgrades, and ongoing maintenance expenses while establishing comprehensive baselines for return on investment calculations. These cost measures should address both one-time implementation expenses and recurring operational costs that influence long-term financial performance.
Cost savings analysis identifies and quantifies financial benefits resulting from digital health initiatives including reduced labor costs, eliminated redundant processes, decreased supply expenses, and avoided costly complications while measuring efficiency gains that translate into direct cost reductions. These savings calculations should be based on documented process improvements and measured operational changes rather than theoretical projections.
Revenue impact assessment examines how digital health initiatives affect organizational revenue including increased patient volume, enhanced service offerings, improved billing accuracy, and reduced revenue cycle costs while identifying new revenue opportunities that result from technology capabilities. These revenue measures should address both direct revenue enhancements and indirect effects that support improved financial performance.
Return on investment calculations provide comprehensive assessment of financial value by comparing total implementation and operational costs against quantified benefits including cost savings, revenue enhancements, and productivity improvements while establishing payback periods and ongoing financial returns. These ROI calculations should address both short-term financial impacts and long-term strategic value that justify continued investment in digital health initiatives.
Technology Performance and Adoption Metrics
Digital health success depends heavily on technology performance and user adoption that must be measured and monitored to ensure that systems operate effectively while meeting user needs and expectations. Technology performance metrics address system reliability, functionality, and user experience while adoption measures track utilization patterns and user acceptance that influence overall program success.
System performance indicators measure technical aspects of digital health platforms including uptime percentages, response times, error rates, and capacity utilization while assessing whether technology infrastructure supports reliable and efficient operation. These performance measures should establish service level standards while providing continuous monitoring that identifies potential issues before they impact user experience or clinical operations.
User adoption tracking measures how healthcare providers and patients utilize digital health tools including login frequency, feature utilization rates, session duration, and user growth patterns while identifying factors that promote or inhibit technology acceptance. These adoption metrics should provide insights into user behavior and preferences while identifying opportunities for training, support, and system optimization.
Usability assessment evaluates user experience with digital health tools including interface design effectiveness, workflow integration success, learning curve requirements, and user satisfaction with system functionality while identifying areas requiring improvement or enhancement. These usability measures should combine quantitative usage data with qualitative user feedback to provide comprehensive assessment of user experience quality.
Integration effectiveness metrics assess how well digital health systems integrate with existing technology infrastructure including data exchange accuracy, workflow continuity, and interoperability performance while measuring the success of technology integration initiatives. These integration measures should address both technical performance and operational impact of system connectivity and data sharing capabilities.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization Strategies
Effective measurement of digital health initiatives requires ongoing processes for analyzing performance data, identifying improvement opportunities, and implementing optimization strategies that enhance program effectiveness and value over time. These continuous improvement approaches must address both systematic performance monitoring and proactive enhancement initiatives that ensure digital health investments continue delivering value as conditions change and opportunities emerge.
Performance trend analysis enables healthcare organizations to identify patterns, trends, and changes in digital health performance over time while recognizing emerging issues and improvement opportunities before they impact program effectiveness. This trend analysis should examine multiple measurement dimensions simultaneously while providing predictive insights that guide proactive management and optimization efforts.
Benchmarking and comparative analysis provide context for digital health performance by comparing results against industry standards, best practices, and peer organizations while identifying opportunities for improvement and optimization based on successful approaches implemented elsewhere. These comparative approaches should address both performance levels and improvement methodologies while providing practical insights for enhancement initiatives.
Stakeholder feedback integration ensures that measurement results and improvement opportunities are informed by perspectives from patients, clinicians, administrators, and other stakeholders who interact with digital health systems while identifying enhancement priorities that address real user needs and preferences. This feedback integration should combine quantitative measurement data with qualitative stakeholder input to guide improvement initiatives.
Optimization planning and implementation establish systematic approaches for translating measurement insights into specific improvement actions while prioritizing enhancement opportunities based on impact potential, resource requirements, and strategic alignment. These optimization processes should provide structured approaches for implementing improvements while measuring the effectiveness of enhancement initiatives.
The future success of digital health initiatives depends increasingly on sophisticated measurement approaches that capture comprehensive value across clinical, operational, financial, and strategic dimensions while providing actionable insights that guide continued investment and optimization decisions. Healthcare organizations that develop and implement effective digital health KPIs metrics measurement capabilities position themselves to demonstrate value, optimize performance, and achieve sustained success in their technology investments while delivering superior patient care and operational excellence.