Stem cell therapy, a cornerstone of regenerative medicine, is poised to transform the treatment of chronic diseases.
This innovative approach exploits the versatility of stem cells, our body’s foundational cells, to potentially heal long-term conditions such as arthritis, cancer, Parkinson’s disease, heart disease, multiple sclerosis, and diabetes.
Despite ethical controversies, particularly concerning embryonic stem cells, the potential for stem cell therapy to repair damaged tissue, mitigate inflammation, and enhance patient well-being is substantial.
Understanding Stem Cells
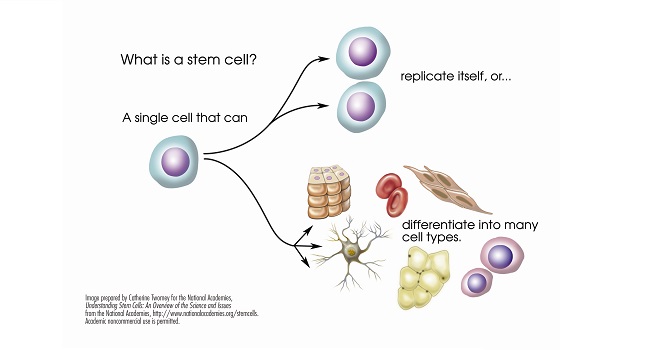
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials from which all other cells with specific functions arise. These cells exhibit pluripotency, which means they can morph into any cell type in the body.
This unique attribute allows stem cells to replace damaged or diseased cells, offering groundbreaking solutions for chronic conditions.
The Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy harnesses the body’s own regenerative capacities to repair damaged tissues and cells. It can stimulate the body’s repair system to grow new, healthy cells, replacing the diseased or dysfunctional ones.
In addition to its regenerative capabilities, stem cell therapy from Cellaxys, for instance, can also reduce inflammation and pain and improve physical function and quality of life for patients. The potential impact of this treatment on chronic disease management is immense.
Stem Cell Therapy for Arthritis
For patients suffering from arthritis, stem cell therapy offers a novel approach to managing this chronic condition by harnessing the body’s ability to repair damaged joint cartilage.
This innovative treatment taps into the regenerative potential of the patient’s own stem cells, which can differentiate into various cell types, to restore joint function and alleviate symptoms.
These cells can reduce inflammation and stimulate the production of cartilage, the smooth elastic tissue that cushions the joints. Furthermore, stem cell therapy provides long-term relief from arthritis symptoms as it addresses the root cause of the condition.
Cancer Treatment With Stem Cells
Stem cell transplants have revolutionized the treatment of cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma by replacing the damaged cells caused by these diseases.
This innovative approach has begun to transform the field of oncology, offering new hope for patients grappling with these debilitating conditions.
- Rejuvenation: Stem cells can rejuvenate the patient’s immune system, enabling it to fight cancer more effectively.
- Precision: The transplanted stem cells can specifically target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells and reducing side effects.
- Flexibility: Stem cell therapy can be tailored to individual patients, offering a personalized approach to cancer treatment.
While still in a relatively early stage of development, stem cell therapy holds immense potential for the future of cancer treatment.
Parkinson’s Disease and Stem Cells
In the realm of neurodegenerative disorders, Parkinson’s disease poses a significant challenge, impacting millions globally. Stem cell therapy emerges as a promising potential treatment.
Fundamental to Parkinson’s is the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to motor and cognitive impairments. Stem cell therapy aims to replace these lost neurons, essentially restoring dopamine production and alleviating symptoms.
Experimental models have demonstrated that stem cells can differentiate into dopamine-producing cells. Transplantation into the brain of Parkinson’s patients has shown some promising early results.
Challenges remain, including controlling stem cell differentiation and addressing potential immune responses. Nonetheless, the potential of stem cells to revolutionize Parkinson’s treatment continues to fuel research and instill hope in patients.
Stem Cell Therapy for Heart Disease
Cardiac diseases, notably heart failure and post-heart attack damage, present a significant global health burden, and emerging research suggests stem cell therapy may offer a revolutionary approach to treatment.
- Regeneration: Stem cells can regenerate and repair damaged heart tissue, improving heart function and patient survival rates.
- Reduced Scarring: Post-heart attack, stem cells have been found to reduce scarring and promote the growth of new blood vessels, preventing long-term cardiac dysfunction.
- Heart Failure Treatment: In cases of heart failure, stem cell therapy can help regenerate lost heart muscle cells, offering a potential alternative to heart transplants.
This therapy, still in the clinical trial phase, presents an exciting frontier in cardiovascular medicine, with the potential to significantly improve outcomes for heart disease patients.
Multiple Sclerosis: A Stem Cell Approach
A progressive neurodegenerative disease, MS damages the protective sheath around nerve fibers, disrupting communication between the brain and body. Stem cell therapy emerges as a promising approach, potentially repairing this neurological damage.
The therapy involves the infusion of stem cells capable of migrating to damaged areas in the brain, aiding in the repair of nerve cells. Furthermore, stem cells may regulate the abnormal immune response characteristic of MS, alleviating symptoms.
While research is ongoing and challenges remain, the prospects of stem cell therapy provide a beacon of hope for those grappling with Multiple Sclerosis.
Stem Cell Therapy in Diabetes Management
Stem cell therapy aims to combat diabetes by using pluripotent stem cells to replace damaged or non-functioning pancreatic beta cells, which are responsible for insulin production.
- Insulin production: Stem cell therapy could enhance the body’s insulin production, thus better controlling blood glucose levels.
- Beta cell regeneration: The process involves stimulating the pancreas to regenerate its own beta cells, potentially reducing the need for external insulin.
- Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes: Stem cell therapy shows promise for both types of diabetes, with studies showing improved blood sugar control and reduced insulin dependency.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy holds the potential to revolutionize chronic disease management.
The unique ability of stem cells to differentiate into various cell types opens new avenues for treating diseases like arthritis, cancer, Parkinson’s, heart diseases, multiple sclerosis, and diabetes.
While ethical controversies exist, particularly regarding embryonic stem cells, the therapeutic benefits cannot be overlooked.
The future of stem cell therapy appears promising, offering hope for long-term solutions to chronic diseases.
FAQs
Can stem cells cure chronic diseases?
Stem cells have shown potential in treating some chronic diseases, but they are not a guaranteed cure. Research is ongoing to determine their effectiveness in various conditions.
What is the survival rate for stem cell therapy?
The survival rate for stem cell therapy varies greatly depending on the disease being treated, the type of stem cells used, and the patient’s overall health. It’s a promising field, but specific rates are continually evolving with ongoing research and clinical trials.
What are the negative effects of stem cell therapy?
Negative effects of stem cell therapy can include reactions at the injection site, infection, and the possibility of the stem cells differentiating into unwanted tissue types. In cases of allogeneic transplants, there can be a risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
What is the success rate of a stem cell transplant?
The success rate of a stem cell transplant also depends heavily on factors such as the type of disease, the patient’s condition, the match of the donor, and the transplant technique. Success rates are improving with medical advancements, yet they remain variable across different situations.



















