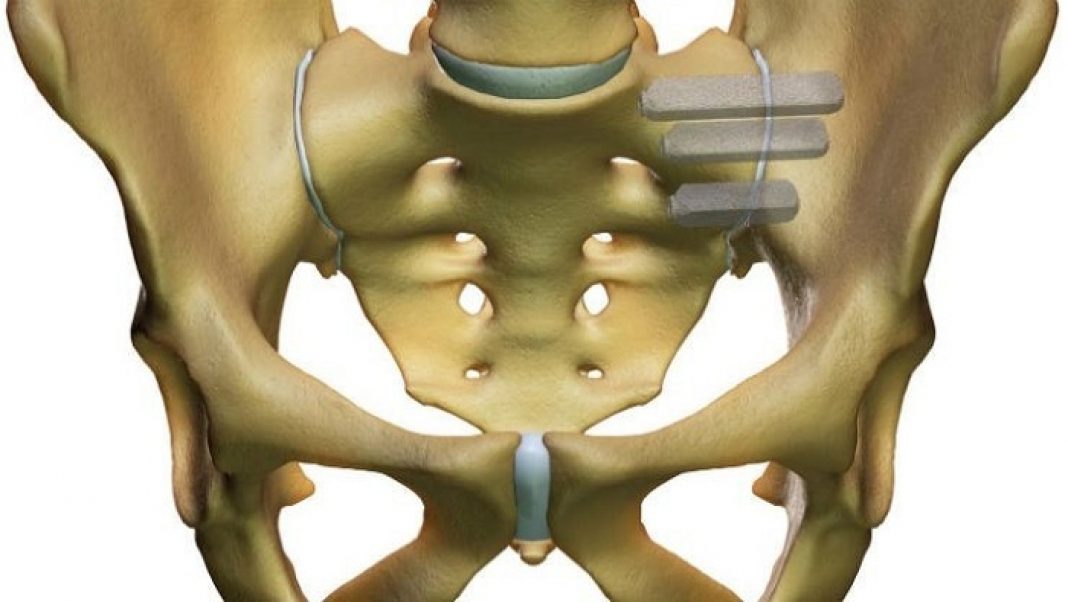
SI-BONE, Inc., a Silicon Valley based medical device company dedicated to solving musculoskeletal disorders of the spinopelvic anatomy, announced that it received an additional 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use of its iFuse Bedrock technology in fusion of the sacroiliac (SI) joint during long construct procedures.
iFuse Bedrock is a technology designed to provide greater stabilization of the joint at the base of long spinal constructs. iFuse was previously cleared by the FDA for sacroiliac fusion using a dorsal, or posterior, implantation approach to treat SI joint dysfunction in patients also undergoing long fusion procedures involving a posterior approach. With this new broader indication, iFuse Bedrock can now be placed across the SI joint as an adjunct to long fusion procedures with the intent of gaining fusion to augment immobilization and stabilization of the SI joint.
“iFuse Bedrock potentially represents an important advancement in how we treat adult deformity patients,” said Dr. Chris Shaffrey, MD, Chief of the Duke Spine Division at Duke University.
Adult spinal deformity surgery represents one of the fastest growing segments of the spine market with an estimated 50,000 procedures per year. Pelvic stabilization of the sacroiliac joint is a well understood clinical need in spinal deformity patients who undergo long fusions to the sacrum.
“The iFuse technology provides spine surgeons with a novel spinopelvic fixation solution for their long construct cases,” said Jeffrey Dunn, President, Chief Executive Officer, and Chairman at SI-BONE. “As we enter the adult deformity market, we remain focused on our commitment to education and clinical evidence that has been the cornerstone of our company, as demonstrated by our 68 peer-reviewed publications including two randomized clinical trials and published long-term data out to six years involving use of iFuse to treat sacroiliac joint dysfunction.”