In this changing environment, cloud computing can be an enabler of organizational transformation. Harnessing the power of the cloud, healthcare organizations can create dynamic infrastructures that improve operational effectiveness and dexterity by optimizing and accelerating IT resource and service delivery.
Clinical and business boundaries can be erased by simplifying access to information, and connecting people as well as business functions across formerly siloed systems, while improving the economics of their IT infrastructure.
Cloud computing—an opportunity for healthcare
Forward-thinking organizations are turning to more advanced technology that can take the information in systems and records and deliver it as cloud computing services. Cloud computing can provide a resilient technology infrastructure that delivers continuously available information-based services. When utilized effectively, cloud capabilities can enable enterprises to become more agile, reduce IT spending, as well as develop and deploy applications faster. Cloud computing can also help reduce energy costs, carbon emissions and the need to expand data centers.1
Because cloud computing automates virtualization, the provisioning process is streamlined and shortened—instead of taking days to weeks of manual provisioning, an automated process can complete the task in minutes. IT infrastructure resources can be delivered more quickly, and the solutions sitting on that infrastructure can be globally available and scale dynamically.
A recent IBM Institute for Business Value study, which surveyed 750 CTOs, CIOs and other technology executives in 19 industries, including healthcare, highlights the strategic importance of the IT infrastructure. Over 70 percent of organizations recognized the important role IT plays in enabling competitive advantage and optimizing revenue and profit. Yet less than 10 percent of respondents reported that their existing IT infrastructure is fully prepared to address the proliferation of mobile devices, social media, data analytics and cloud computing. Despite the stated importance of IT infrastructure, only 22 percent of companies surveyed have a well-defined enterprise IT infrastructure strategy roadmap in place.2
This research highlights the challenges healthcare organizations face as they grapple with the new era of IT. The first step toward transforming the enterprise with cloud computing begins with the preparation of the IT infrastructure for more advanced cloud computing strategies. Complete transformation to the cloud is a journey not limited to infrastructure, though it is a fundamental business shift in how IT services are developed, financed and delivered. Cloud computing enables healthcare organizations to rapidly develop platform services in preparation for the digital health revolution and the growing importance of remote care services utilizing information from the Internet of Things (IoT).3
SaaS helps improve delivery of hospital services
A Canadian hospital needed to streamline clinical processes to improve patient operations and enterprise workflow, while simultaneously providing a mobile experience for clinicians. The hospital was able to reduce implementation time through IBM® BlueWorks Live, a business process management software as a service (SaaS) offering from IBM. Implementing the mobile process-management technology improved the hospital’s throughput and patient experience. The outcome was a 15 percent improvement in staff productivity within three months.4
With the ability to support real-time analytics across data and organizational silos, and address management and cost challenges stemming from exponential growth of data and sprawling infrastructure footprints, cloud computing provides an effective approach for optimizing operations across the entire organization. As a tool for business model innovation, cloud computing can help healthcare organizations meet the imperatives of a transforming industry, to become more efficient, information-driven and patient-centric. Cloud services can help organizations to:
Build sustainable healthcare systems: Create an efficient, flexible organization that proactively manages requirements and opportunities to help overcome the operational challenges of controlling costs, improving efficiency, complying with regulations, optimizing resource utilization, and enabling better visibility across the infrastructure.
 Collaborate to improve care and outcomes: Improve the quality and efficiency of care while cultivating patient centricity by overcoming challenges in the implementation of electronic medical records, promoting collaboration within and among care teams, and integrating secure, trusted information for analytics, evidence-based decision support and personalized care.
Collaborate to improve care and outcomes: Improve the quality and efficiency of care while cultivating patient centricity by overcoming challenges in the implementation of electronic medical records, promoting collaboration within and among care teams, and integrating secure, trusted information for analytics, evidence-based decision support and personalized care.
Increase access to healthcare: Reduce disparities in access and transform inpiduals into advocates for their own health by addressing challenges by analyzing patient needs and behavior, adapting resources and delivery networks to meet these needs, anticipating demands, and delivering services to inpidual consumers and providers
Cloud technology connects hundreds of clinicians for those in need A nonprofit organization is using an IBM cloud-based social business solution that provides collaboration services to a global network of healthcare volunteers. With a focus on Haiti, the solution supports clinicians by giving them immediate access to critical data and information to help support the healthcare needs of the island’s citizens. Using the IBM SmartCloud® for Social Business solution to virtually connect medical workers and volunteers, those on the front lines taking care of patients are armed with an online medical knowledge system that includes treatment options, clinical pathways and best practices specific to the location.5
The benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing technologies are well-suited for organizations looking for proactive ways to meet current healthcare industry challenges. Organizations can use cloud technologies to reveal valuable insights in their data and transform how they make decisions. Cloud solutions can virtually connect healthcare professionals around the globe to collaborate, respond more quickly, enable remote care and share best practices.
Speed: Cloud computing increases the speed of business innovation. Cloud technology supports the development of new applications more quickly than ever before using composable services from a marketplace of APIs. As a result, the organization can gain on-demand access to IT infrastructure resources—including servers and storage networking—and get feedback faster so the business can adjust accordingly. Healthcare organizations can respond more readily to the needs of the business, and the needs of the patients they serve, as well as their partners, suppliers and employees.
Empowerment: Cloud technology is helping healthcare organizations improve and re-engineer their business processes and workflows, as well as increase engagement and collaboration internally and across their enterprise. By freeing application developers to focus on expanding sophistication, rather than administrative and integration challenges, cloud technology helps IT professionals drive optimization and innovation instead of constantly building and maintaining their infrastructure.
Economics: Cloud technology can help improve a healthcare organization’s economics with the ability to bring new capabilities to market ahead of the competition. Using a cloud infrastructure, an organization can buy the IT resources that it needs, when needed, enabling capital to be redeployed by shifting large, upfront expenses to variable expenses. The cloud can also help an organization realize cost savings through automation and standardization.
Across the industry, healthcare organizations are taking a conservative and multi-tiered approach, not focused on either a private cloud or public cloud, but creating a dynamic hybrid cloud infrastructure to combine the best of both worlds to allow flexibility in decision making on deployment models.
In fact, nearly half of all large enterprises will have hybrid cloud deployments by the end of 2017, according to Gartner, Inc.6 Building a hybrid cloud platform allows an enterprise to run applications across on-premises and off-premises environments depending on the needs of the application, data and service provided. Healthcare organizations can transform on-premises capabilities to offer hybrid cloud choices and still maintain an effective governance strategy.
Nationwide cloud infrastructure deployed to improve medical services
To overcome growing operational, management and support issues, a leading healthcare provider with a network of over 20 hospitals in Malaysia engaged IBM to consolidate and centralize its computing infrastructure on the cloud to provide better services to patients and their families. Providing self-service access to information delivered through the cloud also reduced complexity and streamlined operations, allowing the organization to operate at a reduced cost and with greater efficiency, reliability and flexibility. Using cloud technology also facilitated the rollout of new applications to new and existing hospitals. The shift to the cloud will complement the provider’s plan to establish themselves as a major regional player in healthcare services.7
For organizations with large IT investments, hybrid models can help maximize the return on their existing IT investments by transforming IT into self-service private clouds. Hybrid models keep some workloads on the best fit infrastructure and moves others to a public cloud for better economics.
An organization can maintain on-premises control of key applications and data while moving other workloads—such as systems that engage with patients or partners—to the cloud for quick access to data and the expansion of new services. This allows organizations to set up development environments quickly and add new capabilities like analytics or mobile software as a service on the public cloud.
Cloud security and regulatory compliance
The promise of business applications and IT solutions delivered through the cloud is compelling because it can provide new business capabilities on demand. However, it’s important to note that there are significant security and compliance requirements which need to be addressed as part of cloud readiness and governance when using cloud services. These requirements are addressable through robust security, strategic planning and governance.
In the US, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) provisions indicate that healthcare organizations, covered entities (CE), and cloud service providers (CSPs) each bear significant responsibility for regulatory compliance. Regulations regarding protected health data compliance vary by country and not all regulations are clearly defined. Companies looking to globalize business services through the cloud need to consider these variations in regulatory compliance as a significant element of any cloud strategy in terms of evaluating and managing risk across many countries.
As with all large technology programs, a key success factor for cloud strategy is governance and the establishment of enterprise level policies to determine the appropriate workloads to run on the cloud. This requires establishing a management system to assess priorities and the business value of specific workloads. Further, an enterprise cloud strategy will need to reflect an integrated view from both the lines of business and IT. Additional governance would be needed for data and security standards.
As cloud computing provides new opportunities to innovate across the business, it necessitates that organizations continually reassess and enhance their security posture and the risk associated with core digital assets particularly in light of the evolving threat landscape where breaches in health data are increasing and are required to be disclosed to the public in the US.
Based on our experience with clients in healthcare and across all industries, concerns about security can be mitigated by adopting appropriate technologies and implementing plans for continuous risk management. IBM has an extensive security and risk management portfolio that can assist an organization in implementing best practices for security and compliance when adopting a cloud model.These activities span five areas:
Enhance your security and risk posture: Enterprises do this by establishing a security intelligence program, enabling them to derive timely and accurate insight into their security and risk posture.
Protect your data: Given the increase in data breaches, it is important to ensure the security of provider and patient private data at rest, while also achieving visibility and monitoring of appropriate access.
Know your user: Every transaction starts with a user. Verifying a user’s identity and managing access to cloud-based applications and data is foundational to
cloud security.
Ensure integrity of your applications: Application-level attacks are on the rise. Scanning and testing cloud applications for vulnerabilities should be part of the development, operations and continuous delivery processes.
Protect against threats and fraud: Network-level attacks are also a concern and mobile devices can be compromised by malware. A combination of malware protection and network and endpoint security management can help mitigate network-level threats and prevent fraud.
While security and compliance in the past have been inhibitors to cloud services adoption, adopting cloud services have tremendous benefits, including understanding that cloud services providers have a more robust security posture than healthcare organizations are able to adopt on their own, given the complexity of security threat landscape. Strategies to mitigate risk by implementing best practices in security and compliance across people, process and technologies, which also include CSPs, are essential in cloud adoptions and transformation.
A major healthcare insurer’s traditional approach to software development was too slow to comply with fast-changing healthcare reforms. The company also needed to streamline its process for developing and updating applications. Using IBM DevOps Services on the IBM Bluemix™ cloud platform, the company saved USD2.2 million in three pilot development projects in the first six months, while reducing code defects by 80 percent.8
IBM cloud advisory services portfolio
Based on in-depth analysis of a client’s business goals and requirements, IBM cloud advisory services offer a combination of cloud best practices and healthcare expertise to help organizations develop and execute a customized, holistic strategy to use cloud computing—to drive not just savings on IT costs, but to support revenue and growth objectives.
IBM cloud infrastructure strategy and design services can help define a value-driven cloud computing strategy by using rigorous analysis tools. IBM consultants use a unique cloud adoption framework and toolset to help analyze an existing environment and determine which cloud computing model is best suited for an organization. IBM specialists can help clients identify the business areas and workloads that, when migrated to a cloud computing model, facilitate reduced costs and improved service delivery in line with business priorities. IBM can also help determine and address cloud computing’s impact on IT services, organization and governance for a smoother implementation.
IBM Workload Transformation Analysis for Cloud
Developed by IBM Research, this patent-pending analytical tool and methodology is designed to produce a detailed, quantitative analysis of both business applications and infrastructure components. It provides a prioritized list of suitable workloads for migration to the cloud, as well as insight into the potential costs and migration impacts. IBM has used this same tool and methodology for its cloud migration initiatives, narrowing a list of more than 9,500 applications from around the world to those that were best suited for the IBM target cloud. Following this structured approach can enable you to prioritize migration of those workloads to realize the advantages of cloud computing more quickly.
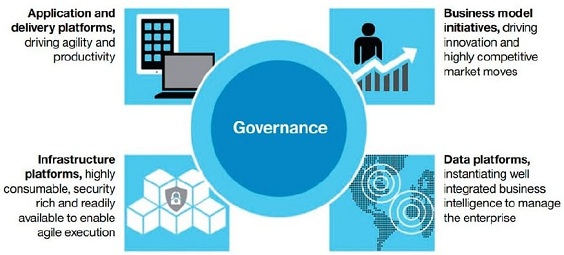
IBM has developed an enterprise cloud strategy framework (Figure 1) to help clients transform their enterprises and work through the complex changes and interactions cloud technologies bring. The framework is designed around four key elements—infrastructure platforms, data platforms, application and delivery platforms, and business models—to be enabled by the cloud. An effective cloud strategy includes governance across the cloud framework, which extends to both external and internal services.
IBM offers a full range of enterprise class infrastructure solutions optimized to build a cloud computing environment. IBM Bluemix is a cloud-based, platform as a service (PaaS) that allows an organization to quickly and dynamically assemble an application using available building blocks, called component services. With BlueMix, developers can move from concept to solution very quickly, using prebuilt components to build an application. Healthcare organizations have not historically developed applications like other industries and therefore have a critical shortage of developer skills when the need for new services is high. Bluemix services can assist with a critical industry skills gap for IT organizations.
Questions you should consider to identify business opportunities for acceleration through cloud:
- What new business strategies and services could cloud enable?
- Where could cloud accelerate a care or service innovation?
- How can cloud help you engage patients differently?
- Which strategic or operational decisions would benefit from big data or compute-intensive analytics that are more feasibly delivered through cloud?
- Where could broader or better connected networks of expertise improve outcomes and business performance?
- How does your cloud strategy enable mobile, social, analytics and big data initiatives?
Conclusion
Transformation of the healthcare industry is accelerating. Cloud computing offers new opportunities for organizations to reshape their business models and services, design innovative ways of providing better, patient-centered care, and empower inpiduals to become active participants in their own care.Healthcare organizations are turning to cloud computing to support new care delivery models and the business capabilities required to navigate the complex technological, regulatory, legislative and cultural shifts occurring in the industry. The flexibility, scalability and access provided by cloud environments make them ideal platforms for information exchange, including the information needs emerging for greater collaboration and personalized patient care in the healthcare industry.
By harnessing the power of cloud computing, healthcare organizations can create dynamic infrastructures that improve operational speed and dexterity by optimizing and accelerating IT resource and service delivery. Cloud is far from being just an IT trend it offers strategic business value that can help healthcare organizations enhance their operations and provide better, more cost-effective patient care.
Why IBM
IBM helps healthcare organizations around the world build private and hybrid clouds and manages millions of cloud-based transactions every day. IBM is unique in bringing together key cloud technologies, deep process knowledge, a broad portfolio of cloud solutions and one of the world’s largest and deepest portfolios of analytics solutions. IBM cloud analytics services and solutions span hardware, software, services and research and are supported by almost 9,000 business analysts and optimization consultants, 400 researchers and a network of global delivery centers. The IBM security portfolio is extensive, integrated and can address many of the concerns in the healthcare industry regarding cloud services adoption.
Continuing the history and leadership of embracing and extending open source technology, IBM contributes to the Cloud Foundry Foundation, the industry’s open platform as a service, which provides a choice of cloud models, frameworks and application services.
Sources / Refrals
1. “Cloud Computing: The IT Solution for the 21st Century.” Carbon Disclosure Project. Verdantix. (2011)
2. “The IT infrastructure conversation.” IBM Institute for Business Value. (July 2014)
3. “Device democracy: Saving the future of the Internet of Things.” IBM Institute for Business Value. (September 2014)
4. “The Ottawa Hospital Achieves Process Innovation with IBM Software.” IBM Client Voices. (April 29, 2012)
5. “IBM Collaborates with Colleagues In Care to Empower Medical Workers in Haiti.” IBM press release. (May 17, 2012)
6. “Gartner Says Nearly Half of Large Enterprises Will Have Hybrid Cloud Deployments by the End of 2017.” Gartner Press Release. (October 1, 2013)
7. “IBM and KPJ Healthcare Berhad Build Nationwide Cloud Infrastructure for Improved Medical Services.” IBM press release. (Mdivay 12, 2014)
8. “A major healthcare company.” IBM press release. (April 8, 2014)