Hospital-at-Home Programs: Implementing Remote Monitoring for Acute Care
The evolution of healthcare delivery has reached a transformative juncture where traditional boundaries between hospital and home care are dissolving, giving rise to innovative models that bring acute-level medical services directly into patients’ homes. Hospital home programs remote monitoring represents one of the most significant paradigm shifts in modern healthcare, fundamentally changing how healthcare organizations deliver complex medical care while maintaining the safety, quality, and clinical oversight that define hospital-level treatment. This revolutionary approach combines advanced monitoring technologies with clinical expertise to create comprehensive care environments that extend far beyond traditional healthcare facility walls.
The emergence of hospital-at-home programs gained unprecedented momentum during the COVID-19 pandemic when healthcare systems worldwide faced capacity constraints that demanded creative solutions for patient management. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services introduced the Acute Hospital Care at Home waiver, recognizing that many conditions traditionally requiring inpatient stays could be safely managed in home environments with appropriate technology and clinical oversight. Today, over 260 hospitals across the United States actively participate in these programs, demonstrating the viability and value of this care delivery model.
Hospital administrators increasingly recognize that successful implementation of hospital home programs remote monitoring requires sophisticated strategies that address technology integration, clinical workflow adaptation, regulatory compliance, and patient safety considerations simultaneously. The complexity of delivering acute care in home environments demands comprehensive planning that encompasses everything from device selection and staff training to emergency response protocols and quality assurance measures. Understanding these multifaceted requirements has become essential for healthcare leaders seeking to develop effective hospital-at-home programs that deliver superior patient outcomes while achieving operational and financial objectives.
Defining the Hospital-at-Home Care Model
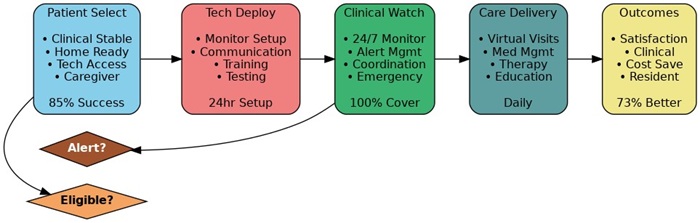
Hospital-at-home programs represent a comprehensive care delivery model that provides hospital-level medical services in patients’ home environments through sophisticated combinations of remote monitoring technology, clinical oversight, and coordinated care teams. These programs extend far beyond traditional home health services to encompass acute care interventions that historically required hospitalization, including intravenous therapy, complex medication management, diagnostic testing, and intensive monitoring of vital signs and clinical parameters.
The distinction between hospital-at-home programs and conventional home health services lies in the intensity and comprehensiveness of care provided, with hospital-at-home models delivering services equivalent to inpatient care while maintaining the comfort and familiar environment of home settings. Patients enrolled in these programs receive continuous clinical oversight through remote monitoring systems that track vital signs, medication adherence, symptom progression, and other critical health indicators in real-time, enabling immediate intervention when clinical conditions change or emergencies arise.
Clinical eligibility for hospital-at-home programs encompasses a wide range of acute conditions that traditionally required inpatient management, including pneumonia, heart failure exacerbations, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease flares, cellulitis requiring intravenous antibiotics, and post-surgical recovery scenarios. The selection criteria focus on patients who are clinically stable enough to be managed outside traditional hospital settings while still requiring intensive monitoring and medical intervention that exceeds the scope of routine home health services.
The operational framework for hospital home programs remote monitoring integrates multiple care delivery components including clinical assessment teams, remote monitoring technology platforms, emergency response systems, medication management services, and coordination with primary care providers and specialists. This comprehensive approach ensures that patients receive seamless, coordinated care that addresses all aspects of their medical needs while maintaining the clinical quality and safety standards associated with hospital-level care.
Reimbursement structures for hospital-at-home programs have evolved to support this innovative care model, with Medicare and many commercial insurers recognizing these services as equivalent to inpatient care for billing and coverage purposes. This reimbursement parity provides financial sustainability for healthcare organizations while creating incentives for program development and expansion across diverse healthcare markets.
Technology Infrastructure and Device Selection
The foundation of successful hospital home programs remote monitoring rests on sophisticated technology infrastructure that seamlessly integrates monitoring devices, communication platforms, data management systems, and clinical workflow applications into comprehensive care delivery ecosystems. The selection and deployment of appropriate monitoring technologies requires careful consideration of clinical requirements, patient capabilities, home environment factors, and integration needs with existing hospital information systems.
Remote monitoring devices for hospital-at-home programs must provide hospital-grade accuracy and reliability while being user-friendly enough for patients and family caregivers to operate effectively in home environments. These devices typically include continuous vital sign monitors that track heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, temperature, and respiratory patterns, along with specialized monitoring equipment for specific conditions such as cardiac rhythm monitors, blood glucose meters, and weight scales for heart failure management.
The communication infrastructure supporting hospital home programs remote monitoring must ensure reliable, real-time data transmission from patient homes to clinical monitoring centers while maintaining redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms that prevent data loss or communication interruptions. This infrastructure typically combines cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth technologies to create robust communication pathways that function effectively across diverse home environments and geographic locations.
Data integration platforms serve as the central nervous system for hospital-at-home programs, collecting information from multiple monitoring devices, correlating data streams, and presenting comprehensive patient status information to clinical teams through intuitive dashboards and alert systems. These platforms must integrate seamlessly with Electronic Health Record systems, clinical decision support tools, and hospital communication systems to ensure that hospital-at-home patients receive the same level of clinical oversight and documentation as traditional inpatients.
The scalability and flexibility of technology platforms become critical considerations as hospital-at-home programs expand to serve larger patient populations and diverse clinical conditions. Successful technology infrastructures must accommodate varying monitoring requirements, support multiple device types and manufacturers, and provide the analytical capabilities necessary for population health management and quality improvement initiatives that drive program optimization over time.
Clinical Workflow Development and Staff Training
The implementation of hospital home programs remote monitoring demands comprehensive redesign of clinical workflows that adapt traditional hospital care processes to distributed care environments while maintaining the clinical quality, safety, and coordination that define effective acute care delivery. This workflow transformation requires careful analysis of existing care processes, identification of technology integration points, and development of new protocols that leverage remote monitoring capabilities to enhance rather than complicate clinical decision-making.
Clinical staffing models for hospital-at-home programs typically involve multidisciplinary teams that include physicians, nurses, pharmacists, and specialized technicians who work collaboratively to provide comprehensive care coordination and clinical oversight. These teams must develop new competencies in remote patient assessment, technology troubleshooting, and virtual care delivery while maintaining their clinical expertise in acute care management and emergency response protocols.
Training programs for hospital-at-home clinical staff must address both technological proficiency and clinical adaptation challenges, providing comprehensive education on remote monitoring systems, virtual patient assessment techniques, emergency response protocols, and communication strategies that ensure effective care coordination across distributed care environments. These programs should include hands-on experience with monitoring technologies, simulation exercises that replicate common clinical scenarios, and ongoing education that keeps pace with technology evolution and clinical best practices.
Documentation and communication protocols for hospital home programs remote monitoring must ensure that all clinical activities, patient interactions, and care decisions are accurately recorded and communicated among care team members while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and quality assurance standards. These protocols should establish clear guidelines for data entry, clinical note completion, care plan updates, and handoff communications that ensure continuity of care across shift changes and care transitions.
Quality assurance processes for hospital-at-home programs must address the unique challenges associated with delivering acute care in uncontrolled home environments while maintaining the clinical outcomes and patient safety standards expected from hospital-level care. These processes should include regular patient assessment protocols, technology performance monitoring, clinical outcome tracking, and continuous improvement mechanisms that identify and address potential issues before they impact patient care quality.
Patient Selection and Enrollment Processes
Effective patient selection represents a critical success factor for hospital home programs remote monitoring because appropriate patient identification ensures that candidates can safely benefit from home-based acute care while avoiding potential complications that might arise from inadequate clinical oversight or inappropriate care settings. The development of comprehensive selection criteria requires careful consideration of clinical factors, social determinants, home environment characteristics, and patient engagement capabilities that influence the likelihood of successful program participation.
Clinical eligibility criteria for hospital-at-home programs must balance the desire to serve diverse patient populations with the need to maintain safety and clinical effectiveness standards that protect patients and ensure positive outcomes. These criteria typically consider factors such as diagnosis-specific requirements, clinical stability indicators, medication complexity, monitoring needs, and potential for clinical deterioration that might require immediate hospital-level intervention.
The assessment of home environment suitability involves comprehensive evaluation of physical space, safety considerations, caregiver availability, technology infrastructure, and emergency access factors that could impact the delivery of safe and effective acute care services. This assessment should include site visits by clinical staff, evaluation of communication capabilities, identification of potential environmental hazards, and verification that necessary support systems are available to ensure patient safety throughout the care episode.
Patient and family engagement assessment becomes crucial for hospital home programs remote monitoring success because effective participation requires active involvement in monitoring activities, medication management, and communication with care teams. The evaluation process should assess health literacy levels, technology comfort, caregiver availability, and motivation factors that influence the likelihood of successful program completion and positive clinical outcomes.
Informed consent processes for hospital-at-home programs must ensure that patients and families fully understand the nature of home-based acute care, the responsibilities associated with program participation, the technology requirements, and the potential risks and benefits compared to traditional hospital care. These consent processes should address emergency procedures, technology troubleshooting, care team communication, and expectations for patient and caregiver participation in monitoring and care activities.
Emergency Response and Safety Protocols
The development of comprehensive emergency response protocols represents one of the most critical aspects of hospital home programs remote monitoring because the ability to provide immediate intervention during medical emergencies directly impacts patient safety and program viability. These protocols must address various emergency scenarios while providing clear guidance for patients, caregivers, and clinical staff regarding appropriate response procedures and escalation pathways.
Emergency detection capabilities integrated into remote monitoring systems must provide reliable identification of critical changes in patient status that require immediate clinical intervention or emergency medical services activation. These capabilities typically include automated alert systems that monitor vital sign parameters, clinical deterioration indicators, and device malfunction signals while providing redundant notification mechanisms that ensure appropriate personnel receive emergency alerts promptly.
Clinical triage protocols for hospital-at-home emergency situations must enable rapid assessment of patient status and appropriate resource allocation while maintaining communication with emergency medical services, hospital emergency departments, and specialist physicians who may need to provide immediate consultation or intervention. These protocols should establish clear decision trees that guide clinical staff through emergency assessment and response procedures while ensuring appropriate documentation and communication throughout the emergency response process.
Patient and caregiver education regarding emergency recognition and response procedures becomes essential for hospital home programs remote monitoring success because immediate recognition of emergency situations and appropriate initial response can significantly impact patient outcomes. This education should cover recognition of warning signs, proper use of emergency communication systems, basic first aid procedures, and coordination with emergency medical services personnel who may not be familiar with hospital-at-home programs.
Coordination with local emergency medical services requires proactive relationship development and communication protocols that ensure emergency responders understand the nature of hospital-at-home programs and can provide appropriate care while maintaining coordination with hospital-based clinical teams. This coordination should include advanced notification systems that alert emergency services to hospital-at-home patients in their coverage areas, along with protocols for information sharing and care transition when emergency transport becomes necessary.
Technology Integration and Interoperability
Successful hospital home programs remote monitoring depend on seamless integration between monitoring technologies, hospital information systems, clinical workflow applications, and communication platforms that enable comprehensive care coordination while maintaining data integrity and clinical oversight. This integration challenge requires sophisticated technical architecture that accommodates diverse device types, communication protocols, and data formats while ensuring reliable performance across varied home environments and network conditions.
Electronic Health Record integration represents a fundamental requirement for hospital-at-home programs because clinical documentation, care planning, and communication must maintain the same standards and accessibility as traditional inpatient care. Remote monitoring data must flow seamlessly into EHR systems while providing clinical staff with comprehensive patient information that supports informed decision-making and appropriate care coordination.
Real-time data processing capabilities become essential for hospital home programs remote monitoring because clinical conditions can change rapidly and require immediate intervention to prevent complications or adverse outcomes. Data processing systems must analyze multiple data streams simultaneously while applying clinical decision support algorithms that identify concerning trends and trigger appropriate alerts and interventions.
The challenge of device interoperability requires careful selection of monitoring technologies that can communicate effectively with existing hospital systems while providing flexibility for future technology evolution and expansion. Standards-based approaches that leverage established healthcare interoperability frameworks help ensure that technology investments remain viable as programs grow and evolve over time.
Cloud-based platform considerations include data security, scalability, reliability, and regulatory compliance requirements that must be addressed while providing the performance and accessibility necessary for effective clinical operations. Healthcare organizations must evaluate cloud platforms carefully to ensure they meet healthcare-specific requirements while providing the technical capabilities necessary for successful program implementation and operation.
Quality Measurement and Outcomes Assessment
Comprehensive quality measurement programs for hospital home programs remote monitoring must demonstrate that home-based acute care delivers clinical outcomes, patient satisfaction, and safety performance that meets or exceeds traditional hospital care standards while providing evidence for continuous improvement initiatives and program optimization. These measurement programs require sophisticated data collection, analysis, and reporting capabilities that address clinical, operational, and financial performance indicators.
Clinical outcome metrics for hospital-at-home programs should encompass traditional healthcare quality indicators such as readmission rates, mortality rates, length of care episodes, and complication rates while incorporating measures specific to remote monitoring effectiveness such as early detection of clinical deterioration, medication adherence, and patient engagement levels. These metrics provide essential evidence for program effectiveness and identify opportunities for clinical improvement.
Patient experience measurement becomes particularly important for hospital home programs remote monitoring because the care delivery model fundamentally changes the patient experience compared to traditional hospitalization. Patient satisfaction surveys should address technology usability, communication effectiveness, caregiver support, and overall care quality while identifying factors that contribute to positive or negative patient experiences.
Safety performance indicators for hospital-at-home programs must address the unique risks associated with delivering acute care in home environments while demonstrating that safety performance meets acceptable standards for healthcare delivery. These indicators should include medication errors, technology failures, emergency response times, and adverse events while providing trending data that identifies potential safety concerns before they impact patient outcomes.
Cost-effectiveness analysis provides essential evidence for program sustainability and expansion by demonstrating the financial value of hospital-at-home care compared to traditional inpatient services. These analyses should consider direct care costs, technology expenses, staff resources, and indirect costs while calculating return on investment and identifying factors that contribute to program financial performance.
The path forward for hospital home programs remote monitoring requires sustained commitment to comprehensive program development that addresses clinical, technological, operational, and financial considerations while maintaining focus on patient safety and care quality. Healthcare organizations that successfully implement these programs position themselves at the forefront of healthcare delivery innovation while providing superior patient experiences and achieving operational efficiencies that support long-term sustainability and growth in an increasingly competitive healthcare marketplace.



















