It is important to understand how to use patient monitors for several jobs and responsibilities. You may be a healthcare professional, working in a hospital or similar environment, or a caregiver that has someone that is connected to such a piece of equipment. You need to understand how to read the monitor in order to properly watch them, monitoring their different vital signs. It is important for those that are unfamiliar, such as nursing and medical students, to gain a grasp and understanding of the monitors in order to prepare for working in a hospital setting.
Setting Up The Patient Monitors
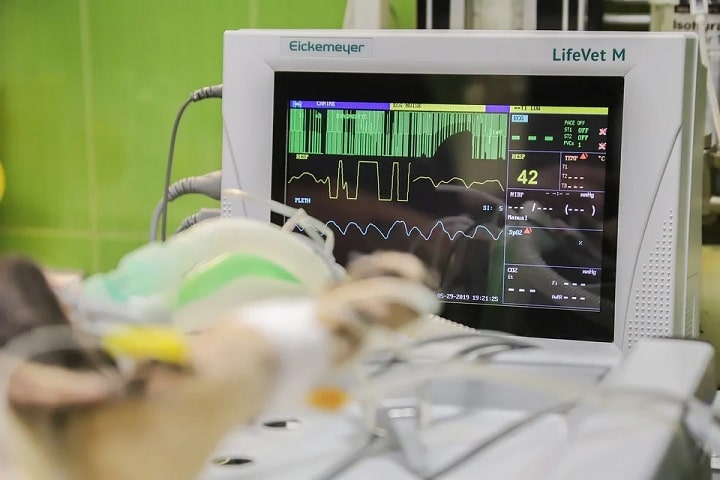
Patient monitors, if operational, will require little time to start up once powered on. They may have lights and indicators to signify the patient status, utilizing the numbers and data to determine if a patient is in need of assistance and should be prioritized for health concerns. When setting up your monitors, you’ll see information that translates to the patient in terms of demographics and ways to identify them to ensure that they are properly treated for whatever they come into the hospital for. These would include basics that are key patient details like their name and age, which would tie in with their health records. The monitors may also indicate the location where they are, specifically the hospital room they are designated in.
Pulse Rate
Although every patient monitor is different, depending on the make and manufacturer of the equipment, there are several components that are more common throughout the devices. When you first look at a patient monitor, you will often see numbers and lines. These are important indicators. The pulse rate, usually indicated by PR, shows the number of beats per minute. The average person will have a heart rate or pulse rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Keep in mind, this number will fluctuate depending on the state of the person. Someone in a resting or relaxed state will have a much lower pulse rate than that of someone going through emotional or physical stress. General fitness and health will also contribute to that number.
Temperature
You will also see temperature shown on patient monitors, as this is an important indicator of a person’s general health. It is important to keep in mind the normal temperature range and use this to observe if someone is above or below that level, indicating a problem that needs to be addressed. Temperature can also change depending on activity, food and liquid consumption, the surrounding environment, as well as changes in a person’s body. Use these external and internal factors in conjunction with body temperature to ensure the patient is of good status.
Blood Oxygen
Blood oxygen is labeled or can be determined on these monitors by the number that shows under SpO2. This will indicate how much oxygen is in the blood, showing a percentage. If the number is below 95, this may show something concerning, as that is the ideal percentage to have in terms of blood oxygen levels. If the number is even lower, below 90 percent, the patient may require oxygen through external means.
Respiration Rate
Under RR on the patient monitor, you can see the respiration rate. This indicates the number of breaths a patient takes in a minute. The typical adult breathes in around 12 to 16 times per minute. It is key to remember that this can change the readings for your patients for various reasons. These will range from their activity, illness, or any type of injury they may have that affects their breathing.
Blood Pressure
There are indicators on the monitor to help evaluate the blood pressure of a patient. 2 numbers are made up of systolic and diastolic data, that collectively provide you information regarding blood pressure levels. Keep in mind that the patient’s blood pressure will fluctuate, and be affected by their emotional and physical state.
Heart Rate Line
The line that is at the top is designated to watch the heart rate. Here, you will be able to see the heart’s functioning on the hospital monitors, seeing the beating and cycles with each wave or spike. These should be relatively consistent, and if there are any irregularities in the patterns of the ECG, or electrocardiogram, this could be caused by underlying issues that need to be looked further into.
Blood Oxygen Flow Line
The next line below the one that indicates heart rate shows blood flow. This is important for issues that deal with circulation. The movement on this line corresponds or typically will match that of the first line, indicating positive oxygen levels with each heartbeat. Issues dealing with this might suggest that your extremities or certain limbs and parts of the body are not getting the required oxygen they need.
Breathing
In addition to the respiratory rate, you can also monitor a patient and their breathing by looking at the wave form, which is typically the third line on the monitors. Here, you can monitor the patient’s breathing closely, watching for changes in breathing pattern and not just in the number itself. This is helpful for looking out for breathing issues when someone has difficulty breathing, or in certain events where the patient stops breathing altogether. Some more basic monitors may not have this, but only have the respiratory rate number to provide you information regarding that person’s breathing. The reason this line is not present in all monitors is that it is only really needed for patients that have issues with breathing. If the patient is in the hospital being treated for other issues, this may not be required or be as essential in certain hospital rooms.
Not all patient monitors are designed the same. It is important that when you are utilizing the monitors that you have to work with, that you understand how to properly operate them and how to decipher the different indicators and data on the screen. This will impact whatever job you have and how to be efficient in your role when monitoring such information.