FDA Publishes Updated AI-Enabled Medical Devices List
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced its extended public list of AI-enabled medical devices, increasing transparency and awareness.
To increase openness and understanding regarding regulated artificial intelligence (AI) technology in healthcare, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) published an enlarged public list of AI-enabled medical devices on July 10, 2025.
The FDA defines AI-enabled devices as those leveraging artificial intelligence or machine learning (AI/ML) for one or more functions integral to clinical care. These devices are either classified as software intended to operate as a medical device (Software as a Medical Device, or SaMD) or are embedded within broader systems.
The AI-Enabled Medical Device List is not merely a catalogue—it is a strategic tool developed to serve multiple stakeholders:
- For developers and digital health innovators: The list offers visibility into how the FDA is evaluating AI technologies, helping shape future innovations and regulatory submissions.
- For hospitals and healthcare providers: It enhances transparency in medical AI, enabling better-informed decisions when adopting new technologies.
- For patients and the public: It clearly signals when medical devices incorporate AI, fostering trust in safety, accuracy, and oversight.
Emphasis on Transparency, Lifecycle, and Foundation Models
In parallel with device authorisations, the FDA is pushing forward several initiatives designed to safeguard patient safety and promote responsible AI development.
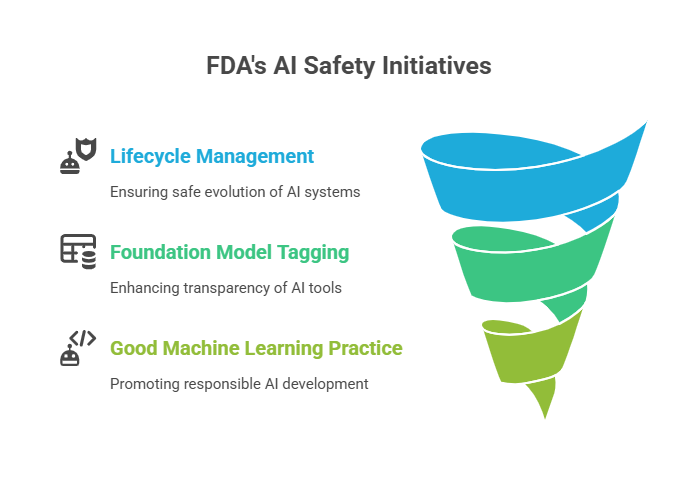
1. Lifecycle Management via PCCPs
The final guidance on Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCPs) supports the safe and predictable evolution of AI systems over time. It allows manufacturers to update algorithms (e.g., via retraining or threshold adjustments) without needing full resubmission—as long as predefined plans and monitoring criteria are approved.
2. Foundation Model Tagging (LLMs)
The FDA also plans to label or flag devices that utilise large language models (LLMs) or multimodal AI architectures, enhancing transparency on how AI tools operate, especially those that process free text, voice, or diverse inputs.
3. Good Machine Learning Practice (GMLP)
The agency continues to encourage adherence to GMLP principles, covering everything from dataset diversity to clinical evaluation and post-market monitoring.
What Hospital Leaders Need to Know
The explosion in FDA-cleared AI devices—211 in under 10 months—isn’t just a regulatory milestone. It’s a call to action for hospital management teams, clinical engineers, and CIOs.
Key Strategic Considerations:
- Procurement & Integration: AI tools must fit into existing EHR/PACS and IT infrastructures, minimising clinician friction.
- Clinical Oversight: Institutions should form AI governance committees to vet tools, review efficacy, and track real-world performance.
- Compliance Monitoring: With PCCPs and evolving guidance, hospitals must track AI system updates and ensure regulatory alignment.
Education & Trust: Staff training and patient communication are critical to the successful adoption of AI-driven care protocols.
What’s New: 211 Devices Cleared Since Sept 2024
Since September 28 2024, the FDA has certified or approved 211 AI-enabled medical devices, demonstrating the rapid adoption of algorithmic intelligence in clinical operations.
According to multiple independent analyses, the radiology panel continues to dominate these new clearances, reflecting both market demand and technological maturity in medical imaging.
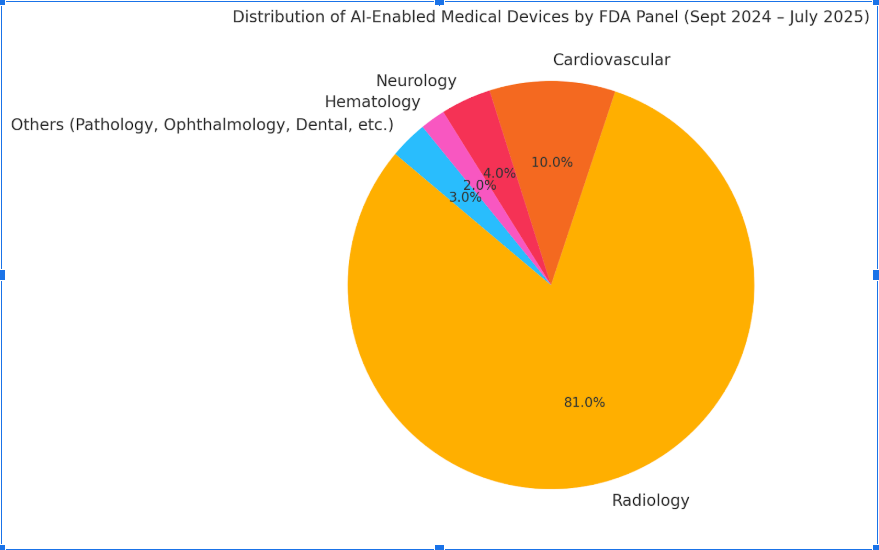
Breakdown by Medical Speciality Panel (July 2025 update):
| Specialty Panel | % of AI Devices |
| Radiology | 81% |
| Cardiovascular | 10% |
| Neurology | 4% |
| Hematology | 2% |
| Pathology, Ophthalmology, Others | 3% combined |
Radiology at the Forefront
The sheer volume of AI devices in radiology is no surprise. Deep learning’s exceptional performance in image classification, anomaly detection, and pattern recognition has made it ideal for applications such as:
- Mammography and breast cancer risk prediction
- Lung nodule detection on CT scans
- Fracture identification in X-rays
- Workflow triage and flagging of critical cases
One standout addition is Clairity’s Allix5 system—a breast cancer risk assessment AI that was granted De Novo authorisation under the newly assigned SEZ product code, marking a significant innovation in preventive oncology.
Other Panels Gaining Ground
Cardiovascular Devices
AI tools in cardiology are emerging in rhythm analysis, echocardiographic image assessment, and heart failure risk scoring. Roughly 10% of the new approvals belong to this category.
Neurology & Hematology
Neurological devices include stroke-detection and seizure-prediction systems, while haematology sees applications in automated cell counting and blood film analysis.
Dental, Ophthalmology & Other Panels
These fields are early adopters of AI-enabled detection tools—e.g., automated caries detection, retinal disease screening, and pathology slide analysis.
Full FDA list is available here: FDA AI-Enabled Medical Devices
Final Takeaway
With this July 10 update, the FDA’s running tally of AI-enabled devices exceeds 840 listings, out of which 211 were added in just the past nine months. While radiology remains the epicentre, a broader shift is underway—signalling that AI’s role in medicine is maturing from niche to necessity.
Hospital leaders must now pivot from exploration to execution—developing robust frameworks to harness this next generation of intelligent healthcare tools for both patient care and operational efficiency.